
#Gaia project galaxy software
The UK is a major partner in DPAC, responsible for the processing of the photometric data (Cambridge data processing centre for Gaia) and the preparation of software for the spectroscopic data processing. The on-ground processing of the science data is the responsibility of the scientific community, organized in the Gaia Data Processing and Analysis Consortium, DPAC. The Mullard Space Science Laboratory of University College London has had a major role in the development of the spectrometer and calibration of the CCDs and their electronics. From the variation with time in the stellar positions, combined with the flux measurements, astronomers can derive some of the most fundamental properties of stars, such as their distances, luminosities and velocities in space.īuilding Gaia has been the responsibility of an industrial consortium led by EADS Astrium in Toulouse, with two major UK partners, Astrium Stevenage (on-board data processing and micropropulsion system) and e2V (CCDs (charge-coupled devices)). Spectra will also be taken of at least 100 million stars. It has been designed to measure with extreme accuracy positions and fluxes of approximately one billion stars on the sky over a period of five to six years.

Gaia was selected by ESA in 2001 and launched on 19 December 2013.
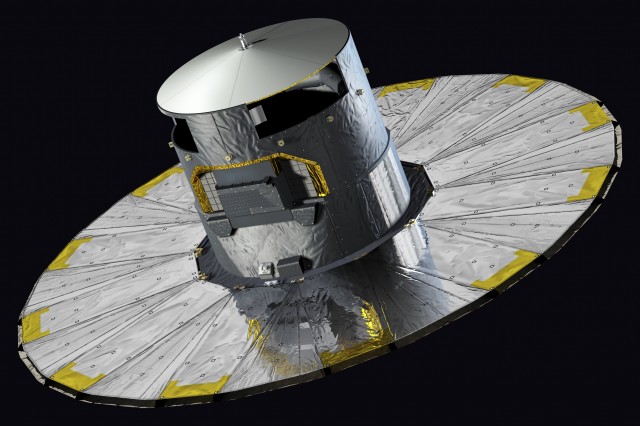
The Gaia satellite is a European Space Agency (ESA) cornerstone project, aimed at the understanding of how our Milky Way galaxy was formed and how it has evolved into what it is today.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
